Critical Thinking in Nursing Practice
Critical thinking plays a crucial role in clinical judgment. For example, when troubleshooting a computer issue, you use logic, prior knowledge, and past experiences to resolve the problem. This process mirrors how nurses apply their clinical knowledge and experience to make decisions in patient care. As a nursing student, developing critical thinking skills helps you approach new patient care situations with creativity and confidence, enabling you to make informed decisions that lead to the best outcomes for patients. Critical thinking is a skill that evolves with time and experience, shaped by a commitment to learning and a proactive approach to problem-solving. This process of developing sound clinical judgment is vital for providing quality care.
By the end of this section, you should know about:
- The nurse’s responsibility in making clinical decisions.
- Critical thinking in general.
- The components of a critical thinking model for clinical decision making.
- Critical thinking skills used in nursing practice.
- The critical thinking attitudes used in clinical decision making.
- How professional standards influence a nurse’s clinical decisions.
- The importance of managing stress when making clinical decisions.
- The relationship of the nursing process to critical thinking.
Let’s take a closer look at them.
Test Your Knowledge
At the end of this section, take a fast and free pop quiz to see how much you know about Critical Thinking in Nursing Practice.
The nurse’s responsibility in making clinical decisions.
Nurse makes clinical decisions based on evidence, patient assessment, and professional values. Considering patient values and preferences This includes ensuring patient safety. Collaborating with the health care team, and providing care appropriate and compassionate to.
Critical thinking in general
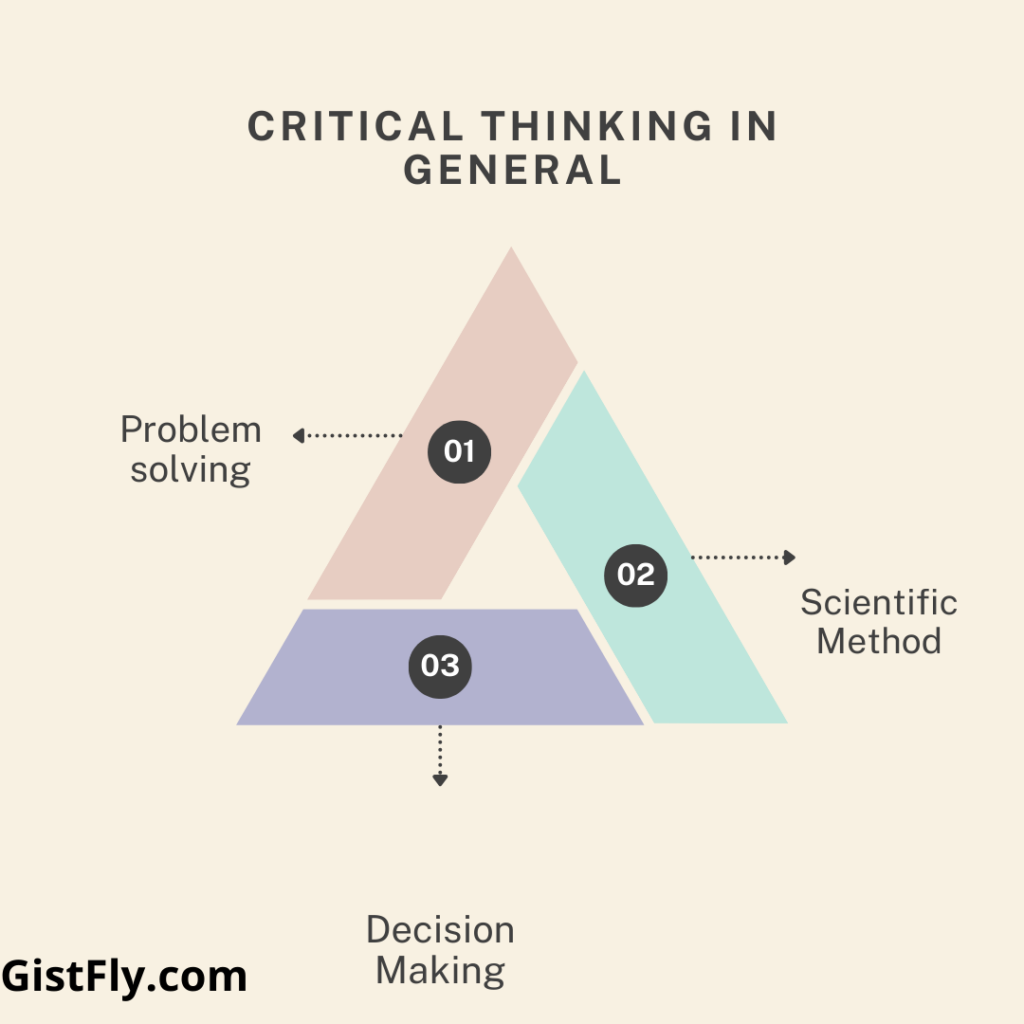
Scientific Method: The scientific method is a systematic approach to problem solving that includes five steps: identifying the problem, gathering data, formulating the hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and testing the results in the results of the view. This approach has been used in research to address behavioral issues in nursing. For example, nurses can examine and use nursing resources such as staff and patient education to reduce cardiac readmissions.
Problem solving: Problem solving involves identifying issues, exploring possible solutions, and evaluating their effectiveness. For example, if a nurse observes a patient struggling with medication adherence, they may recommend the use of clear labels and medication packaging charts to improve compliance
Decision Making: Decision making is a cognitive process that helps nurses choose the best course of action. It involves evaluating options, evaluating them against standards (individual, professional, or institutional), and making appropriate choices. Decision making in clinical practice helps to prioritize patient care needs and select the most appropriate interventions.
Specific Critical Thinking Competencies
Diagnostic Reasoning: Diagnostic reasoning is the process of interpreting patient data to diagnose health problems. This involves identifying symptoms and comparing them to a possible diagnosis. For example, pulmonary fibrosis is thought to be based on symptoms such as dyspnea and chest pain, prompting immediate action to confirm the diagnosis
Clinical Inference: Clinical reasoning is drawing conclusions based on past experiences in diagnostic reasoning. It helps nurses develop plans and predict health issues. For example, if a patient exhibits signs of discomfort, the nurse may assume that the patient is in severe pain and respond appropriately
Clinical Decision Making: Clinical decision making is a high-level process that involves selecting the most effective interventions beyond mere diagnosis. It requires understanding the patient’s specific needs and context, prioritizing care, and making informed decisions. The key is “getting to know the patient,” which includes understanding their physical and emotional responses, and helping to guide individual care decisions.
Clinical Expertise
Knowing the Patient: Expert nurses can identify potential problems quickly by observing subtle changes in a patient’s condition, such as a slight drop in blood pressure. This understanding is based on experience and familiarity with the patient, which leads to faster and more accurate decision-making.
Prioritizing Care: In fast-paced clinical settings, nurses must use critical thinking to prioritize patient needs. This requires evaluating patient conditions, available resources, and the risks associated with treatment delays, ensuring that the most urgent needs are addressed first.
Building Clinical Decision-Making Skills
Foster Relationships: Spending time with patients during assessments and follow-ups helps nurses build rapport, fostering a deeper understanding of the patient’s needs and responses. A strong nurse-patient relationship is crucial for making timely and accurate decisions about care.
Clinical Experience: Continuous interaction with patients provides nurses with valuable clinical experience, helping them recognize patterns and trends in various healthcare situations. This experience enables more informed decision-making over time.
Quality Improvement (QI) and Nursing Practice
Quality improvement (QI) focuses on enhancing patient care and safety. Nurses can apply critical thinking and clinical decision-making in QI projects to improve patient outcomes. For instance, if a nursing unit sees an increase in patient falls. nurses can take a systematic approach to address the issue. Here’s how they might use critical thinking to improve care:
Identify the Problem: Nurses are seeing an increase in patient falls over the past three months. This initial finding prompted in-depth research into the neurological causes of falls and their impact on patient safety.
Gather Data: Nurses collect relevant data, including number of falls, time of day, patient condition, and fall locations. Incident reports, patient charts, and professional advice are available to understand the circumstances associated with each fall.
Analyze the Data: Nurses use critical thinking to analyze the data to identify patterns. For example, falls may be found to occur more frequently with shift changes or in certain patients, such as elderly patients. sedated patients, or patients with disorders of mobility This finding helps guide further interventions.
Formulate Solutions: Based on their assessment, nurses propose solutions to prevent falls. These may include increasing staffing levels during high-risk hours, additional fall prevention training for staff. and introducing safety features such as bed alarms and non-fall socks.
Test Solutions: Nurses implement the proposed solutions and evaluate their effectiveness. For example, bed alarms and fall-proof socks could be tested on a single unit basis to see if these interventions reduce falls.
More QI
Evaluate the Results: After interventions are implemented, nurses evaluate outcomes by comparing fall rates before and after the change. This may include reviewing incident reports, monitoring patient outcomes, and discussing with staff how these interventions impact care.
Make Adjustments: If the interventions do not lead to a significant reduction in falls. nurses use critical thinking to adjust their approach. This may involve revising patient care plans, modifying staff protocols, or trying different fall prevention tools. Further data collection and analysis may also be required.
Foster Collaboration and Patient Involvement: Nurses collaborate with other healthcare team members, such as physicians and physical therapists. This is to ensure that fall prevention measures are comprehensive. They may also involve patients and their families in the prevention plan by educating them about the importance of requesting assistance when needed.
Clinical Decision Making for Group Care
When applying clinical decision-making to a group of patients, nurses on a unit must:
Identify and Prioritize Diagnoses: Nurses assess which patients are at higher risk for falls and prioritize their care based on the severity of their condition and fall risk.
Analyze Patient Needs: Nurses evaluate which patients require immediate attention based on their conditions, the complexity of their issues, and the urgency of interventions.
Manage Resources: Nurses consider the available resources—staff, assistive personnel. and equipment—and allocate them appropriately to ensure adequate support and patient safety.
Delegate Care: To optimize care, nurses may delegate certain tasks. such as taking vital signs or monitoring less critical patients, to nursing assistants. This allows nurses to focus their attention on higher-risk patients and critical interventions
The components of a critical thinking model for clinical decision making.
A critical thinking model for clinical decision making
Critical thinking is essential to developing nursing skills, as it enhances nurses’ ability to work effectively and reduce errors. The model developed by Kataoka-Yahiro and Seiler (1994) highlights five components of critical thinking.
Knowledge Base: This is the information and concepts that prepare nurses to understand the patient’s problem.
Experience: Learning from clinical situations, diagnoses, and patient interactions.
Critical Thinking Competencies: Skills applied to each step of the nursing process.
Characteristics: qualities such as enthusiasm, responsibility and creativity, which guide decision making.
Standards: Opinion and professional standards that ensure the quality and integrity of decisions.
Critical thinking in nursing is not just about knowledge but about how nurses apply their experiences, competencies, and attitudes in making clinical judgments. Nurses must consistently use these components throughout the nursing process to ensure effective patient care.
Critical thinking skills used in nursing practice.
To develop critical thinking skills, it’s important to connect theoretical knowledge to everyday nursing practices. This process can be challenging, as it requires you to apply classroom learning, reading, and dialogues with peers to real-life patient care situations.
Reflective Journaling
Reflective journaling is a key tool for fostering critical thinking. It helps you clarify and understand clinical concepts through reflection. Journaling allows you to express your clinical experiences and thoughts in your own words, which can improve your observation, description, and decision-making skills.
Here are some tips for reflecting on clinical experiences:
Identify Confusion or Interest: What experiences, situations, or information in your clinical practice stand out as confusing, difficult, or interesting?
Analyze Meaning: What was the meaning of the experience? Consider your own feelings as well as those of your patient or their family. What factors influenced the situation?
Make Connections to Past or Future Experiences: Does the situation remind you of past experiences or an ideal future outcome? How does it relate to previous knowledge or future goals?
Link with Nursing Science and Theory: How do the experiences you describe relate to what you have learned about nursing science and theory?
Meeting with Colleagues
Collaboration with colleagues is essential for developing critical thinking skills. Nurses can benefit from regular meetings with faculty, preceptors, or fellow nurses to discuss experiences and validate decisions. These interactions provide opportunities to share different perspectives, ask questions, and receive constructive feedback. Having a formal platform, such as staff meetings or unit practice councils, fosters a supportive environment where experiences are shared, and both good practices and areas for improvement are discussed.
Concept Mapping
Concept mapping is a visual tool that helps nurses organize and synthesize patient data, nursing diagnoses, interventions, and evaluation measures. It offers a holistic view of the patient, illustrating the relationships between various diagnoses and interventions. By creating a concept map, you can identify patterns and connections among patient problems and better understand their clinical situation. Concept maps are particularly useful for comprehensive care planning, helping to ensure that all relevant information is considered and organized in a meaningful way.
The critical thinking attitudes used in clinical decision making.
Critical thinking governs how nurses solve clinical problems and ensure care is effective and patient-centered. Self-confidence is important, as nurses need to be confident in their ability to perform tasks and communicate effectively with patients. Independent thinking includes critical thinking and access to evidence-based solutions to nursing problems, as well as a culture of innovation and improvement. Justice requires that all patients be treated equally, without individual bias, to ensure ethical care. Responsibility and accountability emphasize that nurses are accountable for their actions and decisions, and emphasize the importance of professional integrity.
Risk-taking is another important characteristic, encouraging nurses to try new ways to improve patient outcomes while maintaining safety. Discipline ensures that nurses are thorough and systematic in data collection and decision-making, reducing error and increasing quality of care. Patience is essential when dealing with difficult or unsolved problems, as it leads to the search for effective solutions. Creativity enables nurses to find new strategies when standard approaches do not meet the needs of unique patients. Interviewing, or constantly asking questions about “why,” deepens understanding and helps refine care practices. Integrity requires honesty and high professional standards, while humility allows nurses to recognize their limitations and ask for additional knowledge or support when needed.
Standards of Critical Thinking
Intellectual standards, as described by Paul (1993), are universal principles of rational thought that guide the nursing process. These standards are applied to ensure informed and sound clinical decisions. Precision, accuracy, and consistency are fundamental during data collection, ensuring that all gathered information is clear, correct, and actionable. Logical and significant thinking is essential in care planning, ensuring that the plan is both coherent and relevant to the patient’s needs.
Critical thinking throughout clinical practice ensures that intellectual standards are applied systematically, preventing haphazard or incomplete decision-making. For example, Tonya, a nurse, demonstrates these intellectual standards while anticipating potential clinical issues for her patient, Mr. Lawson. She asks relevant questions about the risks associated with anticoagulation therapy and carefully evaluates the appropriateness of additional pain medication. Her approach highlights logical, precise, and accurate decision-making, exemplifying the application of intellectual standards in practice.
How professional standards influence a nurse’s clinical decisions.
Professional standards refer to ethical standards and evidence-based guidelines that guide nursing practice, ensuring that care is scientifically responsible and ethically relevant Critical thinking in nursing must take into account patients’ personal values and beliefs and promotes their well-being. This means that nursing care must be patient-centered, respecting cultural differences and individual preferences in decision-making.
Evidence-based assessment is an important component of professional standards, as nurses rely on clinical practice guidelines and research findings to inform their clinical decisions These standards help nurses accurately assess a patient’s condition and evaluate how interventions are effective to ensure care is based on recent relevant evidence.
Professional responsibility is another important area, and nurses are guided by standards such as the Nursing Practice Act. These practices set clear expectations for quality health care, ensuring that nurses remain accountable to high standards and meet professional standards essential to their practice.
For example, in the area of pain management, nurses use evidence-based criteria to accurately assess a patient’s pain. This will allow the most appropriate interventions to be selected and their effectiveness evaluated, ensuring patient comfort and well-being while maintaining professional responsibilities in the course of care.
The importance of managing stress when making clinical decisions.
Stress in healthcare settings can significantly affect a nurse’s mental and physiological state. Research has shown that the continuous activation of the sympathetic nervous system due to stress disrupts various cognitive functions, such as decision-making, error detection, speech, memory, and emotional regulation. For example, working long shifts, such as 12-hour shifts, can impair medical judgment because stress impacts attention and focus face stress due to a variety of factors, including witnessing patient suffering, managing multiple responsibilities, and working in fast-paced environments. When stress becomes chronic or extreme, it can result in poor work productivity, impaired decision-making, communication challenges, and a reduced ability to cope with clinical situations.
Based Practice on Stress in Nursing
PICO Question: What are the effects of stressful work environments on thinking and decision-making among acute care nurses compared to those in non-stressful environments?
Evidence Summary: Research highlights the impact of stress on cognitive and emotional functions due to the interaction between regions of the brain such as the cortex, amygdala, and brainstem. Stress in healthcare settings is commonly caused by heavy workloads, management styles, professional conflicts, and the emotional demands of patient care. Stress impairs problem-solving, communication, memory, and emotional regulation. Nurses under stress may experience negative mood shifts, cynicism, frustration, and may inadvertently provide inaccurate information.
Applicative
To manage stress effectively and maintain clear decision-making and communication, nurses can apply the following strategies:
Know when you’re stressed: Watch for physical and emotional signs of stress such as muscle tension, irritability, difficulty concentrating and fatigue
Take your time: Stay away from a stressful situation whenever possible. Do a quick relaxation exercise or find a quiet place away from distractions to refresh your mind and calm you down.
Share stressful experiences: Share difficult patient care situations with trusted colleagues. Not only does this help relieve stress, but it also provides emotional support and common ground.
Participate in decision-making: Participate in the decision-making processes of nursing practice. This promotes self-control, which can reduce stress.
Attend stress management programs: Consider attending stress management classes or workshops offered at your workplace to learn ways to better cope with stress
The relationship of the nursing process to critical thinking.
The nursing process, outlined by the American Nurses Association (ANA), includes five steps: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. The purpose of this process is to diagnose and treat human responses to actual or potential health problems. Nurses apply critical thinking to address a patient’s unique needs and achieve agreed-upon health outcomes.
